Heat and cold therapy, ancient practices with modern applications in regenerative care, offer powerful approaches to healing and recovery. Cold therapy reduces inflammation, slows metabolism, and constricts blood vessels, making it effective for managing pain and speeding muscle recovery after intense physical activities. Heat therapy promotes blood circulation, stimulates endorphin release, and enhances flexibility, benefiting sore muscles, stiff joints, and overall mobility. Alternating heat and cold accelerates tissue repair, reduces injury, and optimizes athletic performance. Integrating these therapies improves recovery rates and complements traditional medical treatments for chronic pain conditions and post-surgery rehabilitation, with practical applications including post-workout recovery and professional athlete training.
“Unleash the power of contrast: exploring the dual benefits of heat and cold therapy in regenerative care. This comprehensive guide delves into the ancient yet innovative practices of thermotherapy, revealing their profound impact on accelerating recovery and fostering tissue regeneration. From the icy depths of cold therapy, which reduces inflammation and pain, to the warming embrace of heat therapy, we unravel the science behind these techniques. Prepare to discover how integrating both enhances therapeutic outcomes, offering a holistic approach to optimal health and swift recovery.”
- Understanding Heat and Cold Therapy: A Basic Overview
- The Role of Cold Therapy in Accelerating Recovery Processes
- Heat Therapy: Unlocking the Potential for Tissue Regeneration
- Integrating Heat and Cold: Enhancing Therapeutic Outcomes
- Practical Applications and Future Perspectives in Regenerative Care
Understanding Heat and Cold Therapy: A Basic Overview

Heat and cold therapy have long been used in various cultures, but their modern application in regenerative care offers a powerful approach to healing and recovery. This ancient practice leverages the dual benefits of heat and cold to stimulate physiological responses, enhancing the body’s natural ability to heal itself.
Cold therapy for recovery is well-documented, with exposure to cold temperatures reducing inflammation, slowing down metabolism, and constricting blood vessels. It has been shown to be effective in managing pain and speeding up muscle recovery after intense physical activities. Conversely, heat therapy promotes blood circulation, stimulates the release of endorphins, and enhances flexibility, making it beneficial for sore muscles, stiff joints, and improving overall mobility. By alternating between heat and cold, regenerative care practitioners aim to accelerate tissue repair, reduce injury, and optimize athletic performance.
The Role of Cold Therapy in Accelerating Recovery Processes

Cold therapy has emerged as a powerful tool in regenerative care, offering significant advantages in accelerating recovery processes. By subjecting the body to controlled cold exposure, either through ice baths, cryotherapy chambers, or even simple ice packs, we can trigger several beneficial physiological responses. One key mechanism is the reduction of inflammation, which is often at the root of many healing challenges. Cold therapy helps constrict blood vessels, decreasing blood flow to affected areas and reducing metabolic waste products that can hinder recovery.
Furthermore, cold stimulation promotes the release of endorphins, our body’s natural painkillers, providing analgesic effects and improving overall comfort during the healing process. This dual action—inflammation reduction and pain management—makes cold therapy an invaluable component in regenerative care routines, enhancing the body’s ability to mend and rejuvenate itself naturally.
Heat Therapy: Unlocking the Potential for Tissue Regeneration
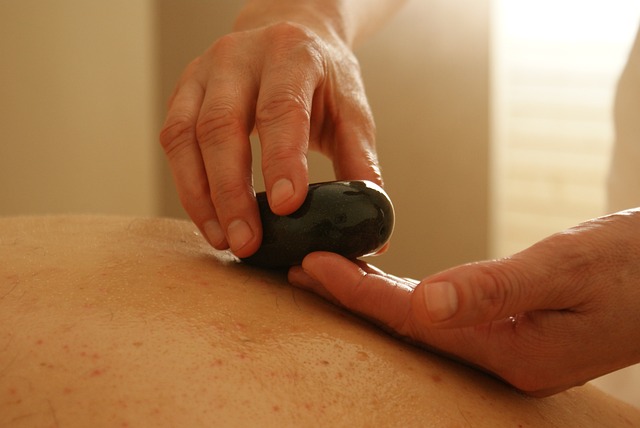
Heat therapy, a time-honored practice in many cultures, has gained significant attention in the field of regenerative care. Its potential to stimulate tissue regeneration is unlocking new possibilities for healing and recovery. When applied as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, heat can promote blood circulation, encouraging the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to damaged areas. This increased vascularity facilitates a robust immune response, clearing away debris and fostering an environment conducive to cell growth and repair.
Moreover, heat therapy can help reduce inflammation and muscle tension, common impediments to recovery after injury or surgery. By using targeted applications of heat, such as hot packs or hydrotherapy, patients can experience relief from pain and discomfort, enabling them to engage more effectively in rehabilitation exercises. This dual benefit—promoting regeneration while mitigating symptoms—makes heat therapy a valuable tool in the arsenal of regenerative care practices, complementing other approaches like cold therapy for recovery, to achieve optimal healing outcomes.
Integrating Heat and Cold: Enhancing Therapeutic Outcomes

Integrating heat and cold therapy is a powerful strategy in regenerative care, offering enhanced therapeutic outcomes. This ancient practice leverages the contrasting effects of hot and cold to stimulate various physiological responses, promoting faster recovery from injuries and inflammation. Heat increases blood flow, enhancing nutrient delivery and waste removal, while cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs pain receptors, providing immediate relief.
By alternating between heat and cold, caregivers can create a dynamic environment that supports the body’s natural healing processes. This method facilitates tissue repair, accelerates cell regeneration, and improves overall recovery rates, making it an effective complement to traditional medical treatments, especially in managing chronic pain conditions and post-surgery rehabilitation.
Practical Applications and Future Perspectives in Regenerative Care

In practical applications, heat and cold therapy are increasingly being integrated into regenerative care routines. Cold therapy, specifically, has shown remarkable potential in accelerating tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and promoting cellular regeneration. It is commonly employed post-workout or after traumatic injuries to minimize muscle soreness and hasten recovery times. Additionally, cold therapy for recovery has gained traction in professional sports, where athletes use ice baths or cryo-saunas to swiftly eliminate metabolic waste and restore muscle function.
Looking ahead, future perspectives in regenerative care suggest a more precise and personalized approach to heat and cold therapy. Advancements in technology are enabling the development of targeted thermotherapy devices that can deliver specific temperature profiles to affected areas, enhancing therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, ongoing research explores the synergistic effects of combining heat and cold treatments with other regenerative modalities, aiming to optimize healing processes and expand the arsenal of tools available in regenerative medicine.
In conclusion, heat and cold therapy represent a powerful duo in regenerative care, offering dual benefits that accelerate recovery processes and enhance tissue regeneration. Cold therapy’s ability to reduce inflammation and pain is well-documented, while heat therapy stimulates blood flow and promotes the healing process. Integrating these modalities not only improves therapeutic outcomes but also opens up exciting practical applications for the future of regenerative care, leveraging the natural power of both heat and cold to restore and rejuvenate the body.